Did you know that about 296 million people worldwide live with chronic hepatitis b (HBV)? This serious liver disease affects millions of lives. It’s a global health challenge that can hit anyone, no matter their age or background.
Hepatitis B is a strong viral infection that attacks the liver. It poses serious health risks. Knowing about this disease is key to protecting yourself and your loved ones from its dangers.
Your liver is a key defense against infections, and HBV attacks it. Learning about how it spreads, how to prevent it, and how to manage it can greatly help protect your health.
Key Takeaways
- HBV is a widespread viral infection affecting millions globally
- The liver disease can be acute or chronic
- Vaccination provides effective protection against HBV
- Early detection and treatment are essential for managing the infection
- Lifestyle choices can significantly impact HBV transmission risks
Understanding Hepatitis B (HBV) and Its Impact on Global Health
The hepatitis b virus is a big problem worldwide, affecting millions. Knowing about it can help stop it from spreading and lessen its effects on health.
Global Statistics and Demographics
Chronic hepatitis hits about 296 million people globally. It’s most common in Asia and Africa. The numbers show how big of a health issue it is:
- Nearly 1 in 3 people worldwide have been exposed to hepatitis B
- 15-25% of chronic infections lead to liver cancer
- Most infections happen in adults through blood and bodily fluids
Economic Burden of HBV
The cost of hepatitis b virus is huge. Healthcare spends billions on treatments and prevention. Direct medical costs and lost productivity weigh heavily on the economy.
“Preventing hepatitis B is not just a medical necessity, but an economic imperative.” – World Health Organization
Public Health Implications
Chronic hepatitis can lead to serious health problems, like liver cancer. Health efforts include vaccines, screenings, and education to cut down on spread and improve care.
- Universal vaccination programs
- Improved screening methods
- Community education efforts
How the Hepatitis B Virus Spreads: Transmission Routes and Risk Factors
It’s important to know how hepatitis B spreads to stay safe. This virus can move through many ways, so being aware is key.
The main ways hepatitis B is passed on include:
- Blood-to-blood contact
- Sexual transmission
- Mother-to-child transfer during childbirth
- Sharing contaminated needles
Blood contact is the most direct way to spread this virus. People like healthcare workers, those with many partners, and drug users are at the biggest risk.
“Prevention starts with understanding how hepatitis B can spread,” says Dr. Sarah Chen, infectious disease specialist.
Groups at high risk need to watch out for possible exposures:
- Healthcare professionals
- Individuals with multiple sexual partners
- People traveling to regions with high hepatitis prevalence
- Intravenous drug users
- Infants born to infected mothers
The hepatitis b surface antigen (hbsag) can live outside the body for a long time. So, keeping clean and taking precautions is vital to stop the virus from spreading.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Hepatitis B Infection
It’s important to know the signs of Hepatitis B early. This liver disease can show different symptoms, from mild to severe. Knowing these signs helps you get medical help quickly.
Early Warning Signs
When you first get Hepatitis B, you might feel a bit off. These early signs are often mild and easy to miss. They include:
- Mild fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Slight muscle aches
- Mild stomach discomfort
Advanced Symptoms
As Hepatitis B gets worse, you’ll notice more obvious symptoms. These signs are more serious and include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
“Early recognition of Hepatitis B symptoms can significantly improve treatment outcomes.” – CDC Hepatology Department
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms of Hepatitis B are urgent and need immediate care. Look out for these critical signs:
| Symptom | Potential Indication |
|---|---|
| Severe abdominal pain | Liver inflammation |
| Persistent jaundice | Advanced liver damage |
| Excessive bruising | Compromised liver function |
If you see any of these signs, call your doctor right away. Quick diagnosis can stop serious problems from this liver virus.
The Different Stages of Hepatitis B Infection
Understanding hepatitis B’s progression is key to managing your health. The infection goes through distinct stages that affect your long-term health.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection has a complex pathway. It can be divided into two main phases: acute hepatitis and chronic hepatitis.
Acute Hepatitis B Phase
- Occurs immediately after virus transmission
- Typically lasts 2-12 weeks
- Most people’s immune systems clear the virus naturally
In acute hepatitis, your body battles the virus. Some people have mild symptoms, while others don’t show any signs.
Chronic Hepatitis B Progression
If the immune system can’t clear the virus in six months, acute hepatitis turns into chronic hepatitis. This stage is very risky for your health.
| Chronic Hepatitis Stage | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Immune Tolerant Phase | High viral replication, minimal liver damage |
| Immune Active Phase | Increased liver inflammation, potential damage |
| Inactive Carrier Phase | Low viral levels, reduced liver inflammation |
“Early detection and monitoring are critical in managing hepatitis B infection.” – CDC Hepatitis Research Team
Chronic hepatitis can cause serious liver problems if not treated. Regular doctor visits and advice are vital for managing it well.
Keeping track of hepatitis B’s progression needs teamwork with healthcare experts. They can understand your specific stage and suggest the right actions.
Diagnosing HBV: Tests and Procedures
Finding out if you have hepatitis B virus (HBV) needs a detailed check. Doctors use many tests to see if your liver is affected and if you have the hepatitis b surface antigen (hbsag).
Getting a correct diagnosis means going through several special tests. These tests help figure out how bad the virus is and how it’s affecting your liver.
Blood Tests and Markers
Blood tests are key in finding HBV. They look for important signs that show if the virus is there:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (hbsag) screening
- Antibody tests for immune response
- Viral load measurement
- Hepatitis B e-antigen analysis
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests show how much damage HBV has done. They check certain enzymes and proteins to see how well your liver is working:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Albumin levels
- Bilirubin concentration
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests give doctors a clear view of your liver. They might suggest:
- Ultrasound scans
- Fibroscan technology
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
“Early detection of hepatitis B can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent long-term liver complications.” – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Knowing about these tests helps you work better with your doctors. Together, you can manage liver disease well.
Treatment Options for Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B
Understanding your treatment options is key when facing a viral infection like hepatitis B. The way to manage chronic hepatitis depends on its stage and severity.

For acute hepatitis B, most people get better without special treatment. Your doctor might suggest:
- Rest and enough water
- Good nutrition
- Checking your liver function
Chronic hepatitis B needs a more detailed approach. Antiviral drugs are key in controlling the virus and stopping liver damage.
“Early intervention can significantly improve long-term liver health outcomes.” – Hepatology Research Center
The main treatments include:
- Antiviral Medications: These drugs slow down virus growth
- Immune System Modulators: Help your body fight the virus
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of liver health and virus levels
Your treatment will depend on several things. These include how active the virus is, liver damage, and your overall health.
| Treatment Category | Primary Goal | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Antiviral Therapy | Suppress Viral Replication | 1-5 Years |
| Immune Modulators | Boost Immune Response | 6-12 Months |
| Supportive Care | Manage Symptoms | As Needed |
Always talk to a healthcare professional. They can help find the best treatment for your chronic hepatitis B.
Preventing Hepatitis B Through Vaccination and Lifestyle Changes
Keeping yourself safe from the hepatitis b virus is key. Knowing how to prevent it can greatly lower your risk. This helps keep you healthy for a long time.
Stopping hepatitis b virus spread needs a mix of medical steps and personal actions. Getting vaccinated is the best way to fight this serious liver disease.
Vaccination Schedule
The hepatitis b vaccine plan changes based on age and risk:
- Newborns: First dose within 24 hours of birth
- Infants: Complete series by 6-18 months
- Children and Adolescents: Three-dose series if not previously vaccinated
- Adults in high-risk groups: Complete vaccination series
Preventive Measures
There are also important lifestyle steps to take:
- Practice safe sexual behavior
- Avoid sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes
- Use protective equipment when handling blood
- Screen sexual partners for hepatitis b virus
“Prevention is always better than cure” – A fundamental principle in managing hepatitis b infection.
Consult your healthcare provider to develop a personalized prevention strategy tailored to your specific health needs and risk profile.
Living with Chronic Hepatitis B: Management and Self-Care
Managing chronic hepatitis B is all about protecting your liver and staying healthy. Your daily choices can really affect how your liver disease progresses and your quality of life.
“Knowledge and proactive management are your best allies in living with chronic hepatitis B”
Here are some key strategies for managing chronic hepatitis:
- Regular medical monitoring
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Avoiding alcohol and harmful substances
- Managing stress levels
- Getting adequate rest
Eating the right foods is very important for people with chronic hepatitis B. Choose foods that help your liver stay healthy:
| Food Category | Recommended Foods | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits/Vegetables | Leafy greens, berries, citrus | Antioxidant protection |
| Proteins | Lean meats, fish, legumes | Cellular repair |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, brown rice | Sustained energy |
Taking your medications as directed is also key. Always talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment and liver function tests.
Your lifestyle choices can really impact how your chronic hepatitis B progresses. By staying informed, eating well, and working with your doctors, you can manage your liver disease and improve your health over time.
Complications of Untreated Hepatitis B
Untreated hepatitis B puts your liver at risk for serious problems. The virus can cause severe issues that harm your health and life quality.
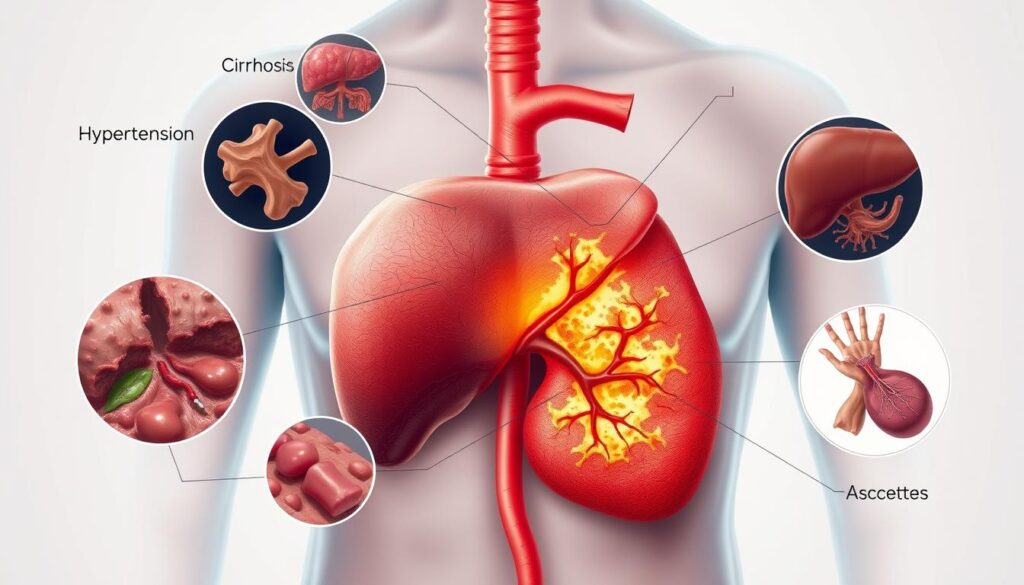
Hepatitis B can lead to severe liver diseases if not treated. Knowing these risks is key to managing your health.
Cirrhosis Development
Chronic hepatitis B can cause cirrhosis. This is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. It makes your liver work poorly.
- Cirrhosis reduces liver cell regeneration
- Liver function becomes progressively compromised
- Scar tissue interferes with blood flow
Liver Cancer Risk
Untreated hepatitis B raises your risk of liver cancer. The virus creates a place for cancer cells to grow.
| Risk Factor | Probability |
|---|---|
| Chronic HBV without treatment | 15-40% lifetime liver cancer risk |
| Treated chronic HBV | 5-10% lifetime liver cancer risk |
“Early detection and consistent medical management are your best defense against hepatitis B complications.” – CDC Hepatitis Research Team
Regular check-ups, antiviral treatments, and healthy habits can lower your risk. Taking care of your health is the best way to fight these serious problems.
Special Considerations for Pregnant Women and Newborns
Pregnancy brings unique challenges for women with hepatitis b virus. It’s important to understand the risks and how to prevent them. This is key for keeping both mother and child safe during this time.
Pregnant women with hepatitis b virus need special care. Finding out early and getting vaccinated can greatly lower the risk of passing it to their babies.
- Screening for hepatitis b is recommended during early pregnancy
- Mothers with active infection need specialized prenatal care
- Newborns require immediate protective interventions
“Prevention is the most effective strategy for protecting infants from hepatitis b transmission” – CDC Hepatitis Specialists
Vaccination is key in stopping hepatitis b virus from being passed from mother to child. Babies born to infected mothers should get:
- Hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth
- Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG)
- Additional vaccine doses at recommended intervals
| Transmission Risk | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| High maternal viral load | Antiviral treatment during pregnancy |
| Active infection at delivery | Immediate infant vaccination |
| Chronic hepatitis b | Regular monitoring and medical supervision |
Medical professionals recommend comprehensive screening and proactive vaccination to protect both maternal and infant health when hepatitis b virus is present.
Natural and Alternative Therapies for Supporting Liver Health
Managing liver disease and chronic hepatitis needs a full approach. Natural therapies are key in helping your liver stay healthy and improving your overall health.
“Your liver is a resilient organ that responds positively to holistic care and lifestyle modifications.” – Dr. Michael Roizen
Diet is crucial for liver health, even with chronic hepatitis. Here are some dietary tips:
- Eat foods high in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and nuts
- Lower your intake of processed sugar and saturated fats
- Drink plenty of water and herbal teas
- Add liver-friendly herbs like milk thistle and turmeric to your diet
Some herbal supplements might help your liver. Milk thistle, for instance, has silymarin, which protects the liver. Always talk to your doctor before taking any supplements.
Changing your lifestyle can also help manage liver disease:
- Try stress-reducing activities like meditation
- Keep up with regular exercise
- Make sure to get enough sleep
- Drink less alcohol
While natural therapies can aid liver health, they should not replace medical treatment for chronic hepatitis.
When to Seek Medical Help and Emergency Care
Knowing when to see a doctor is key for managing hepatitis B (HBV). If you have symptoms like constant tiredness, belly pain, or jaundice, see your doctor right away. Early action can stop serious problems and help your treatment work better.
Some signs need quick medical help. Look out for severe symptoms like extreme weakness, yellow skin or eyes (jaundice), dark pee, clay-colored poop, or uncontrolled bleeding. These could mean serious liver damage and need fast doctor’s care to avoid serious risks.
Regular health checks are vital for those with hepatitis B. Your doctor can check your liver, see if the disease is getting worse, and change your treatment plan. Pregnant women, people with weak immune systems, and those with liver issues should see their doctor more often for better health care.
Being proactive in your health means talking openly with your doctor. If you notice any unusual health changes or have ongoing symptoms from hepatitis B, reach out to your doctor. Acting quickly can greatly improve your health and treatment results.



MOa hqiFq RTik lYiKkwc TbI